-
Star Chart!
Watch this first and answer the questions below.
Here is some more information on Annie Jump Cannon
Annie Jump Cannon!
Write in your journals what Annie Jump Cannon did to help in astronomy.
Draw this chart and write down and answer the questions below using your reference tables.
This represents the H-R Diagram.
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram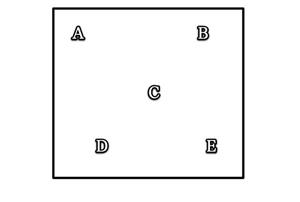
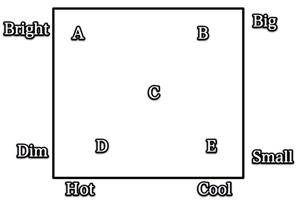
Label the x-axis with temperature and the y-axis with brightness.1. Large, cool stars are found near the letter B.
2. Small hot stars are found near the letter D.
3. Main sequence stars would contain which of the letters above? A, C, and E
4. The brightest and hottest stars will be found at letter A.
5. Which letter represents the position closest to where our sun is plotted? C.
Now label the axis of your diagram and check your answers above.
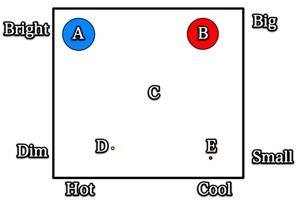
Draw the red and blue stars, as shown below.
Circle the groups of stars that form in your reference tables.
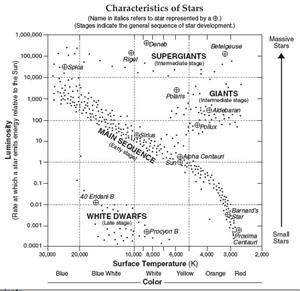
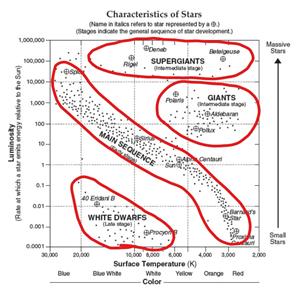
Use the H-R diagram on your reference tables to answer the following.
Finish these statements using the H-R Diagram.
6. The name of the brightest star on the chart is Deneb.
7. The coolest-named star in the Main Sequence is Proxima Centauri.
8. What type of star is Polaris? Giant Star
9. What star is about 25 times brighter than our sun? Sirius
H-R Diagram
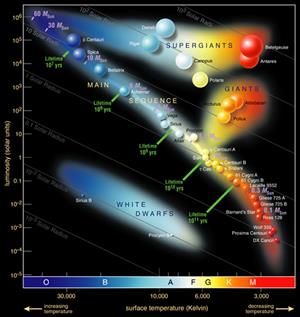
A star's life cycle depends upon its mass.
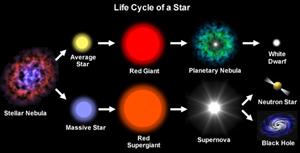
Massive stars burn up quickly and explode, sending their newly formed elements into the cosmos.
Smaller stars (like our sun) can be formed from their newly fused elements.
10. List the life cycle stages of an average-sized star (like the Sun)
1. Stellar Nebula (cloud of interstellar dust)
2. Protostar- Forming star, accumulating mass due to gravity
3. Main Sequence Star- Nuclear Fusion begins in the Protostar's core (Hydrogen fuses to form Helium)
4. Red Giant-star runs out of hydrogen and creates heavier elements (becomes bigger and cooler on its surface)
5. Planetary Nebula-star sheds off its outer layers into space
6. White Dwarf-the very hot (at first) but the much smaller core of the star that slowly fades away.
Reflection
What is the H-R diagram, and what can it tell us about stars?The H-R diagram plots a star's temperature versus brightness and tells us about stars' life stages.
Bonus: Take notes on the following and answer the questions.
Barns Are Painted Red Because of the Physics of Dying Stars
Have you ever noticed that almost every barn you have ever seen is red? Here's why.By Rose Eveleth
Have you ever noticed that almost every barn you have ever seen is red? There’s a reason for that, and it has to do with the chemistry of dying stars. Seriously.
Yonatan Zunger is a Google employee who decided to explain this phenomenon on Google+ recently. The simple answer to why barns are painted red is because red paint is cheap. The cheapest paint there is, in fact. But the reason it’s so cheap? Well, that’s the interesting part.
Red ochrea—Fe2O3—is a simple iron and oxygen compound that absorbs yellow, green, and blue light and appears red. It’s what makes red paint red. It is really cheap because it’s really plentiful. And it’s really plentiful because of nuclear fusion in dying stars. Zunger explains: The only thing holding the star up was the energy of the fusion reactions, so as power levels go down, the star starts to shrink. And as it shrinks, the pressure goes up, and the temperature increases until, suddenly, it hits a temperature where a new reaction can get started. These new reactions give it a big burst of energy but start to form heavier elements still. So the cycle gradually repeats, with the star reacting further and further up the periodic table, producing more and more heavy elements as it goes. Until it hits 56, at that point, the reactions stop producing energy at all; the star shuts down and collapses without stopping.
This incredibly quick collapse triggers the star to explode violently, causing a Supernova!
The Supernova sends the guts of the star in all directions.
As soon as the star hits the 56 nucleons (total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus) cutoff, it falls apart. It doesn’t make anything heavier than 56. What does this have to do with red paint? Because the star stops at 56, it winds up making a ton of things with 56 nucleons. It makes more 56 nucleon-containing things than anything else (aside from the super light stuff in the star that is too light to fuse).
The element that has 56 protons and neutrons in its nucleus in its stable state? Iron. The stuff that makes red paint.
And that, Zunger explains, is how the death of a star determines what color barns are painted.
1. Explain why we paint barns red and how that is related to the stars!
For more information, go to smithsonian.com
http://science.nasa.gov/astrophysics/focus-areas/how-do-stars-form-and-evolve/
Stars
Stars are the most widely recognized astronomical objects and represent the most fundamental building blocks of galaxies. The age, distribution, and composition of the stars in a galaxy trace the history, dynamics, and evolution of that galaxy. Moreover, stars are responsible for manufacturing and distributing heavy elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Their characteristics are intimately tied to the characteristics of the planetary systems that may coalesce about them. Consequently, the study of the birth, life, and death of stars is central to the field of astronomy.
Star Formation
Stars are born within the clouds of dust and scattered throughout most galaxies. A familiar example of such a dust cloud is the Orion Nebula revealed in vivid detail in the adjacent image, which combines images at visible and infrared wavelengths measured by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and Spitzer Space Telescope. Turbulence deep within these clouds gives rise to knots with sufficient mass that the gas and dust can begin to collapse under their own gravitational attraction. As the cloud collapses, the material at the center begins to heat up. Known as a protostar, it is this hot core at the heart of the collapsing cloud that will become a star one day. Three-dimensional computer models of star formation predict that the spinning clouds of collapsing gas and dust may break up into two or three blobs; this would explain why most of the stars in the Milky Way are paired or in groups of multiple stars.
As the cloud collapses, a dense, hot core forms and begins gathering dust and gas. Not all of this material ends up as part of a star — the remaining dust can become planets, asteroids, or comets or may remain dust.
In some cases, the cloud may not collapse at a steady pace. In January 2004, an amateur astronomer, James McNeil, discovered a small nebula that appeared unexpectedly near the nebula Messier 78, in Orion's constellation. When observers around the world pointed their instruments at McNeil's Nebula, they found something interesting — its brightness appears to vary. Observations with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory provided a likely explanation: the interaction between the young star's magnetic field and the surrounding gas causes episodic increases in brightness.
Main Sequence Stars
A star the size of our Sun requires about 50 million years to mature from the beginning of the collapse to adulthood. Our Sun will stay in this mature phase (on the main sequence shown in the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram) for approximately 10 billion years.
The nuclear fusion of hydrogen fuels stars to form helium deep in their interiors. The outflow of energy from the star's central regions provides the pressure necessary to keep the star from collapsing under its weight and the energy by which it shines.
As shown in the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram, Main Sequence stars span a wide range of luminosities and colors and can be classified according to those characteristics. The smallest stars, known as red dwarfs, may contain as little as 10% the mass of the Sun and emit only 0.01% as much energy, glowing feebly at temperatures between 3000-4000K. Despite their diminutive nature, red dwarfs are by far the most numerous stars in the Universe and have lifespans of tens of billions of years.
On the other hand, the most massive stars, known as hypergiants, may be 100 or more times more massive than the Sun and have surface temperatures of more than 30,000 K. Hypergiants emit hundreds of thousands of times more energy than the Sun but have lifetimes of only a few million years. Although extreme stars such as these are believed to have been common in the early Universe, today they are extremely rare - the entire Milky Way galaxy contains only a handful of hypergiants.
Stars and Their Fates
In general, the larger a star, the shorter its life, although all but the most massive stars live for billions of years. When a star has fused all the hydrogen in its core, nuclear reactions cease. Deprived of the energy production needed to support it, the core begins to collapse into itself and becomes much hotter. Hydrogen is still available outside the core, so hydrogen fusion continues in a shell surrounding the core. The increasingly hot core also pushes the star's outer layers outward, causing them to expand and cool, transforming the star into a red giant.
If the star is sufficiently massive, the collapsing core may become hot enough to support more exotic nuclear reactions that consume helium and produce various heavier elements up to iron. However, such reactions offer only a reprieve. Gradually, the star's internal nuclear fires become increasingly unstable - sometimes burning furiously, other times dying down. These variations cause the star to pulsate and throw off its outer layers, enshrouding itself in a cocoon of gas and dust. What happens next depends on the size of the core.
Average Stars Become White Dwarfs
For average stars like the Sun, the process of ejecting its outer layers continues until the stellar core is exposed. This dead but still ferociously hot stellar cinder is called a White Dwarf. White dwarfs, which are roughly our Earth's size despite containing the mass of a star, once puzzled astronomers - why didn't they collapse further? What force supported the mass of the core? Quantum mechanics explained. Pressure from fast-moving electrons keeps these stars from collapsing—the more massive the core, the denser the white dwarf formed. Thus, the smaller a white dwarf is in diameter, the larger it is in mass! These paradoxical stars are very common - our own Sun will be a white dwarf billions of years from now. White dwarfs are intrinsically very faint because they are so small and, lacking a source of energy production, they fade into oblivion as they gradually cool down.This fate awaits only those stars with a mass up to about 1.4 times the mass of our Sun. Above that mass, electron pressure cannot support the core against further collapse. Such stars suffer a different fate as described below.
White Dwarfs May Become Novae
If a white dwarf forms in a binary or multiple-star system, it may experience a more eventful demise as a nova. Nova is Latin for "new" - novae were once thought to be new stars. Today, we understand that they are, in fact, very old stars - white dwarfs. If a white dwarf is close enough to a companion star, its gravity may drag matter - mostly hydrogen - from that star's outer layers onto itself, building up its surface layer. When enough hydrogen has accumulated on the surface, a burst of nuclear fusion occurs, causing the white dwarf to brighten substantially and expel the remaining material. Within a few days, the glow subsides, and the cycle starts again. Sometimes, particularly massive white dwarfs (those near the 1.4 solar mass limits mentioned above) may accrete so much mass in the manner that they collapse and explode completely, becoming what is known as a supernova.Supernovae Leave Behind Neutron Stars or Black Holes
Main sequence stars over eight solar masses are destined to die in a titanic explosion called a supernova. A supernova is not merely a bigger nova. In a nova, only the star's surface explodes. In a supernova, the star's core collapses and then explodes. In massive stars, a complex series of nuclear reactions lead to iron production in the core. Having achieved iron, the star has wrung all the energy it can get out of nuclear fusion - fusion reactions that form elements heavier than iron actually consume energy rather than produce it. The star no longer has any way to support its own mass, and the iron core collapses. In just a matter of seconds, the core shrinks from roughly 5000 miles across to just a dozen, and the temperature spikes 100 billion degrees or more. The star's outer layers initially begin to collapse along with the core but rebound with the enormous release of energy and are thrown violently outward. Supernovae release an almost unimaginable amount of energy. For a period of days to weeks, a supernova may outshine an entire galaxy. Likewise, all the naturally occurring elements and a rich array of subatomic particles are produced in these explosions. On average, a supernova explosion occurs about once every hundred years in the typical galaxy. About 25 to 50 supernovae are discovered each year in other galaxies, but most are too far away to be seen without a telescope.Neutron Stars
If the collapsing stellar core at the center of a supernova contains between about 1.4 and 3 solar masses, the collapse continues until electrons and protons combine to form neutrons, producing a neutron star. Neutron stars are incredibly dense - similar to the density of an atomic nucleus. Because it contains so much mass packed into such a small volume, the gravitation at the surface of a neutron star is immense. Like the White Dwarf stars above, if a neutron star forms in a multiple star system, it can accrete gas by stripping it off nearby companions. The Rossi X-Ray Timing Explorer has captured telltale X-Ray emissions of gas swirling just a few miles from the surface of a neutron star.Neutron stars also have powerful magnetic fields that can accelerate atomic particles around their magnetic poles, producing powerful radiation beams. Those beams sweep around like massive searchlight beams as the star rotates. If such a beam is oriented so that it periodically points toward the Earth, we observe it as regular pulses of radiation that occur whenever the magnetic pole sweeps past the line of sight. In this case, the neutron star is known as a pulsar.
Black Holes
If the collapsed stellar core is larger than three solar masses, it collapses completely to form a black hole: an infinitely dense object whose gravity is so strong that nothing can escape its immediate proximity, not even light. Since photons are what our instruments are designed to see, black holes can only be detected indirectly. Indirect observations are possible because the gravitational field of a black hole is so powerful that any nearby material - often the outer layers of a companion star - is caught up and dragged in. As matter spirals into a black hole, it forms a disk that is heated to enormous temperatures, emitting copious quantities of X-rays and Gamma-rays that indicate the presence of the underlying hidden companion.From the Remains, New Stars Arise
The dust and debris left behind by novae and supernovae eventually blend with the surrounding interstellar gas and dust, enriching it with the heavy elements and chemical compounds produced during stellar death. Eventually, those materials are recycled, providing the building blocks for a new generation of stars and accompanying planetary systems.Summarize the above and explain Carl Sagan's statement
“We are star stuff which has taken its destiny into its own hands.” ― Carl Sagan
Stars

