-
Earth Science Journal!
#13
Title: Looking Back at the Big Bang!
Would you please write down and answer these questions in your journal?
1. What is the Sun made of?
Mostly hydrogen
2. What state of matter is the Sun?
Plasma
3. How do we know if we can't go there?
Sunlight spectra

The Photosphere!
https://www.universetoday.com/144808/this-is-the-highest-resolution-image-ever-taken-of-the-surface-of-the-sun/Check out the link above!
Light from the stars tells us many things!
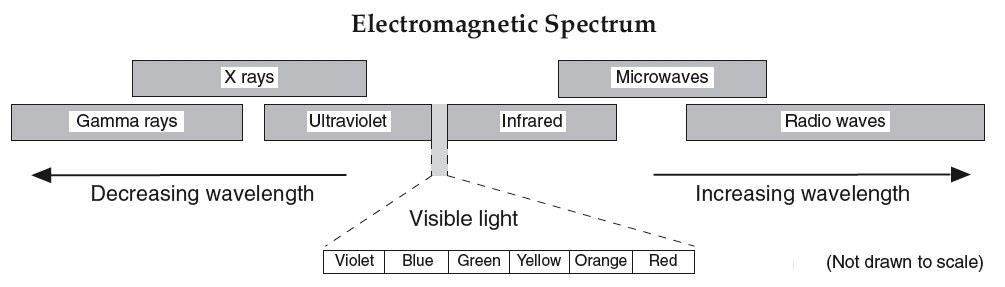
4. What is wavelength?
Please draw and label this wave.
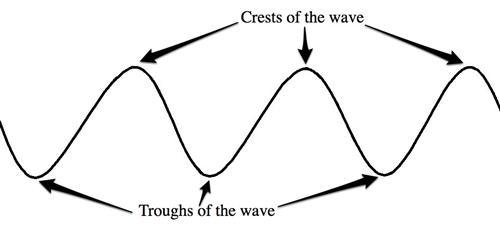
Wavelength- the distance between two crests or troughs on a wave.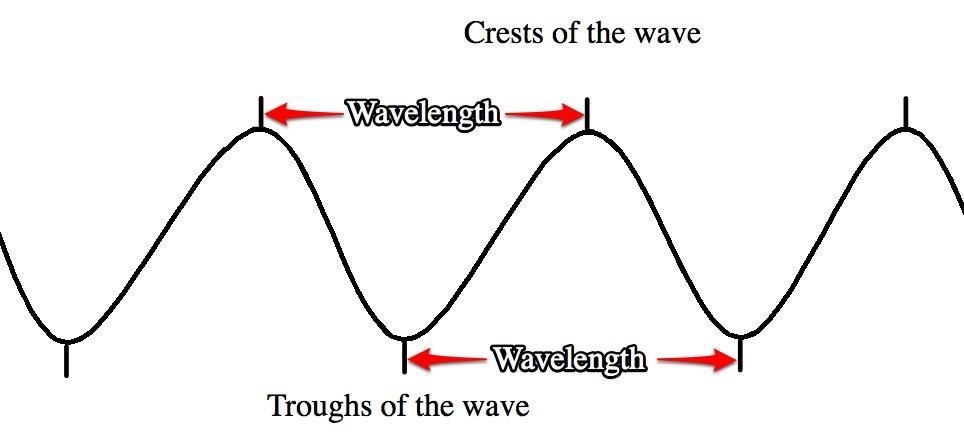
5. What has a longer wavelength, Red or Blue light?
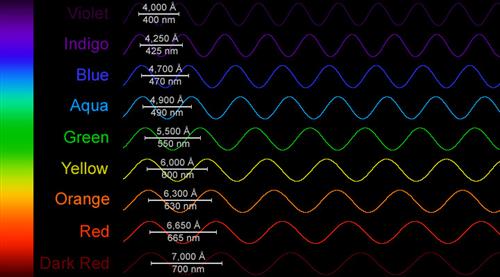
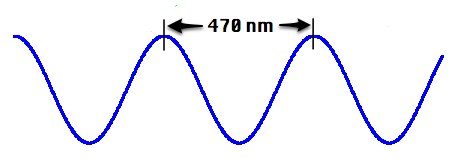
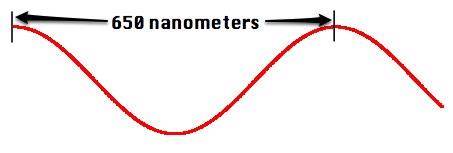
Red light has a longer wavelength than blue light!
6. Which wavelength is generally more dangerous (shorter or longer)? Why?

Shorter wavelength is more dangerous!
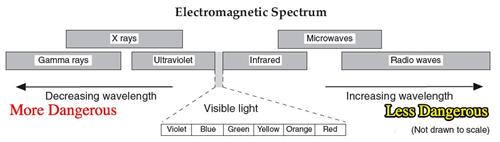
Slinky and laser demo.
7. What form of energy has a slightly longer wavelength than Red? Infrared
 What do you think is in the bag?
What do you think is in the bag?
We can see through the bag by looking at the infrared wavelength.Infrared is also commonly known as heat!
We cannot see infrared energy, but we can feel it as heat!
PREDATOR!8. Why was Arnold "invisible" to the Predator?
Because he was covered with mud making him cool.
Seeing infrared!
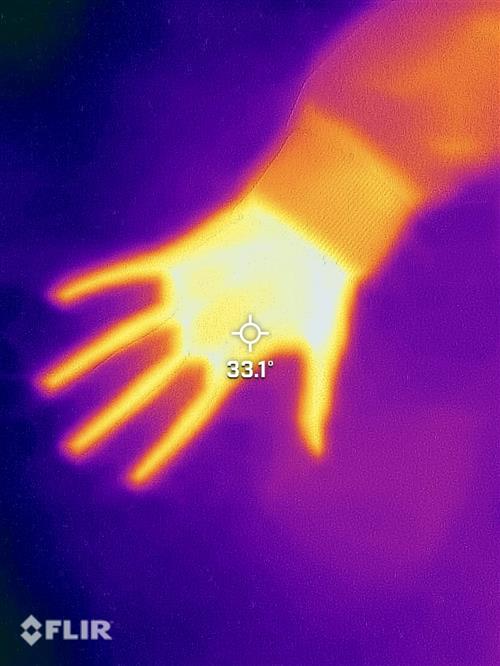

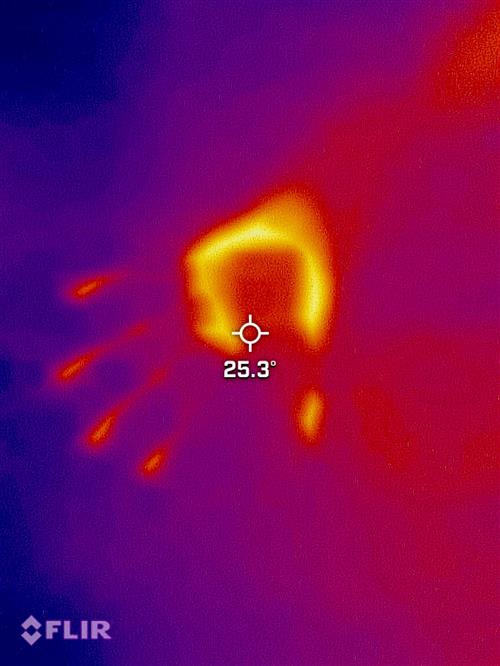
The left photo is of a hand on a student's desk.
The right photo is the heat left after the hand has been taken away!
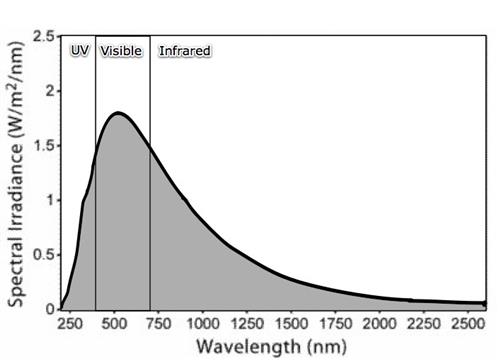
Sunlight reaching the Earth.
Please draw this box.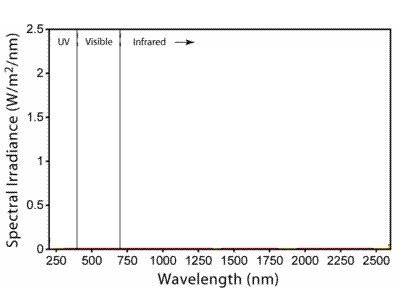
9. Which wavelength of energy reaches the Earth in the greatest amount?
Visible Light!This is why most animals on Earth see in visible light!
They have adapted to the conditions that are best fit for their environment.
Some animals can "see" infrared (like the Predator).
10. What animals do you think can see heat?
Why?
These creatures evolved to become best fit for their environment.
Creatures that can see in infrared
Snakes
Snakes such as boa constrictors and pit vipers use infrared to see their prey. These snakes can see the body heat coming off their victims through the infrared spectrum, allowing them to strike with deadly accuracy.
Fish
Fish such as piranha and goldfish can see in infrared light. This is useful to them in murky waters, where the shorter rays of the color spectrum are scattered, and the longer infrared rays can go further in the water.
Mosquitoes
The mosquito uses infrared to find the blood-rich parts of its prey, allowing it to suck the blood and get out before being noticed. Mosquitoes primarily use sight and smell until they get within 10 feet of their prey, at which point heat vision takes over.
Note: Infrared heat is being trapped in our atmosphere!
During the day, the insolation that reaches the Earth from the sun heats the Earth's surface. At night, heat (infrared) is radiated back into space as the Earth turns away from the Sun. Greenhouse gases like CO2 and methane trap that heat, so the Earth cannot cool down as much as it once did.
This leads to Global Warming (Climate Change).
This is why the Earth is warming more at nighttime than in the day.
Why is Venus so hot?
Venus is so hot because it is surrounded by a very thick carbon dioxide atmosphere, which is about 100 times more massive than our atmosphere here on Earth. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, it heats the surface of Venus. Most of this heat cannot escape into space because it is trapped by the thick CO2 atmosphere.
The heat becomes trapped and builds up to extremely high temperatures. This trapping of heat by the atmosphere is called the greenhouse effect because it is similar to how the glass in a greenhouse traps heat. The greenhouse effect on Venus causes its surface temperature to reach 900 degrees Fahrenheit, making Venus the hottest planet in the entire Solar System!We do not want to be like Venus!
11. What type of energy do these tanning booths mostly give off?

Ultraviolet radiation
12. Why do our bodies tan when we spend time in these booths?
Our bodies tan to try to protect themselves from harmful ultraviolet rays.
Tanning beds now listed among top cancer risks
http://www.usatoday.com/news/health/2009-07-28-tanning-cancer_N.htm
"The risk of skin cancer jumps by 75% when people begin using tanning beds before the age of 30."
They found that tanning beds are as deadly as tobacco.
Light is so Psychedelic!
If we look at light through special glasses (spectroscopes), we can unwrap a lot of information!
Unwrapped light can be read like a barcode when you buy your groceries!

Except for the barcode lines from the Universe are in color!

What element is shining above?

13. What can these spectral lines tell us about starlight?
These barcodes can tell us many things about stars.
Here are some of the most important.1. The temperature (how hot it is)
2. The composition (what it is made of)
3. How it is moving (speed and direction)
Spectra for

 The most abundant element in the Universe!The Big Bang mainly made only hydrogen!
The most abundant element in the Universe!The Big Bang mainly made only hydrogen!
Spectra for

We found Helium on the Sun before we discovered it on the Earth!Helium was discovered in the Sun before it was found on Earth. Pierre-Jules-César Janssen, a French astronomer, noticed a yellow line in the Sun's spectrum while studying a total solar eclipse in 1868. Sir Norman Lockyer, an English astronomer, realized that this line, with a wavelength of 587.49 nanometers, could not be produced by any element known at the time. http://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele002.html
fUSioN = SUN
Stars make the rest of the elements through nuclear fusion!
The remaining elements only compose 2% of the matter in the Universe!Many stars exploded to create that 2%!14. How can we tell a star's or galaxy's speed or direction?
These spectral lines tell us that as well!
It is not the distance between the lines or their brightness; instead, it is how all the lines are "shifted" towards the red or blue end of the spectrum.
This is called the Doppler Effect!
Watch the following.
This is an apparent shift due to relative motions!
http://hmxearthscience.com/Warehouse/astronomy/universe/Universe%20Animations/Doppler_Nav.swf
Let's draw some spectral shifts!
You need a red, blue, and green crayon, along with a small scrap sheet of paper.
Draw the following in your journal.
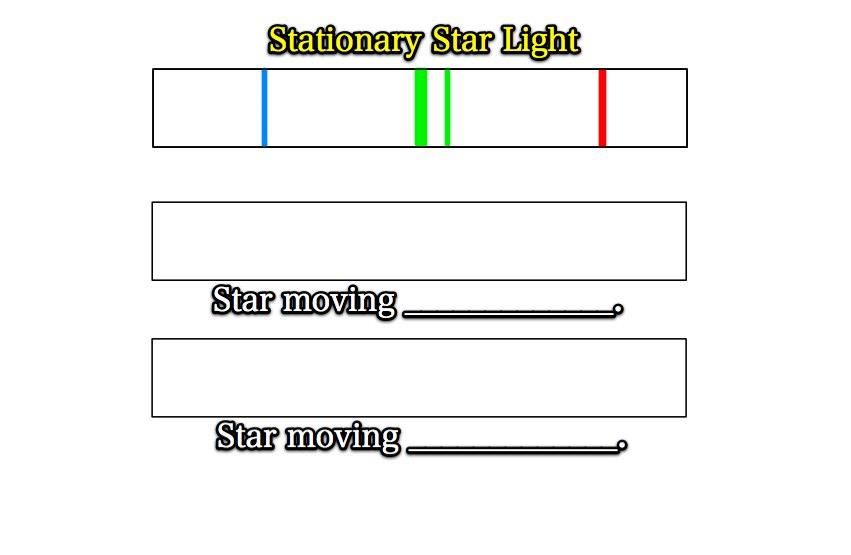
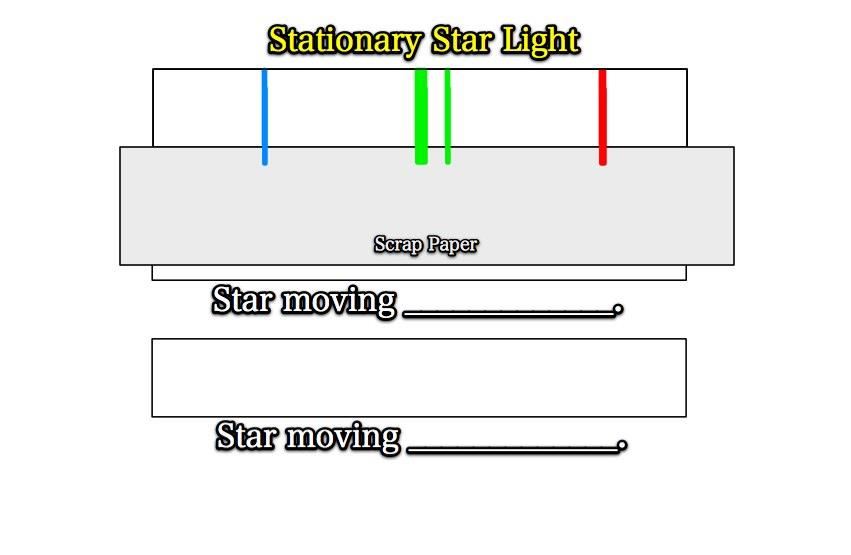
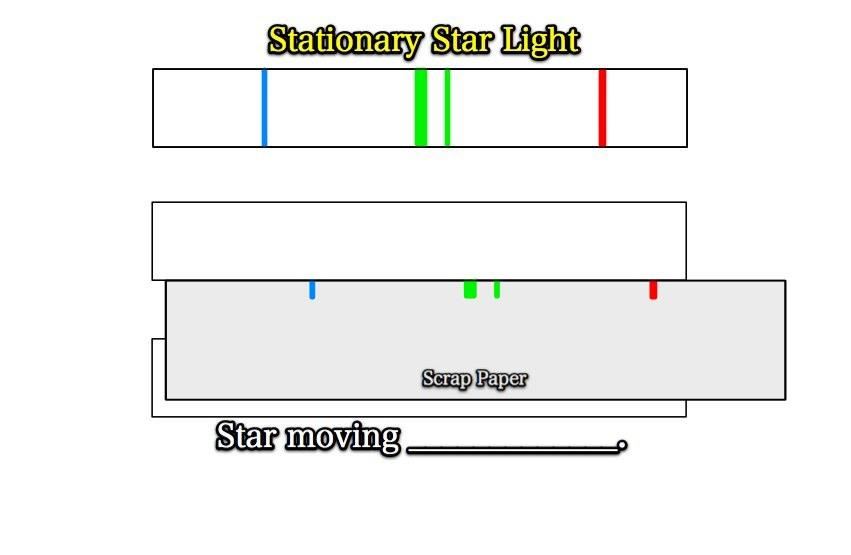
Take your scrap paper and transfer your colored lines onto the middle rectangle,
but shifted over a bit to the right.
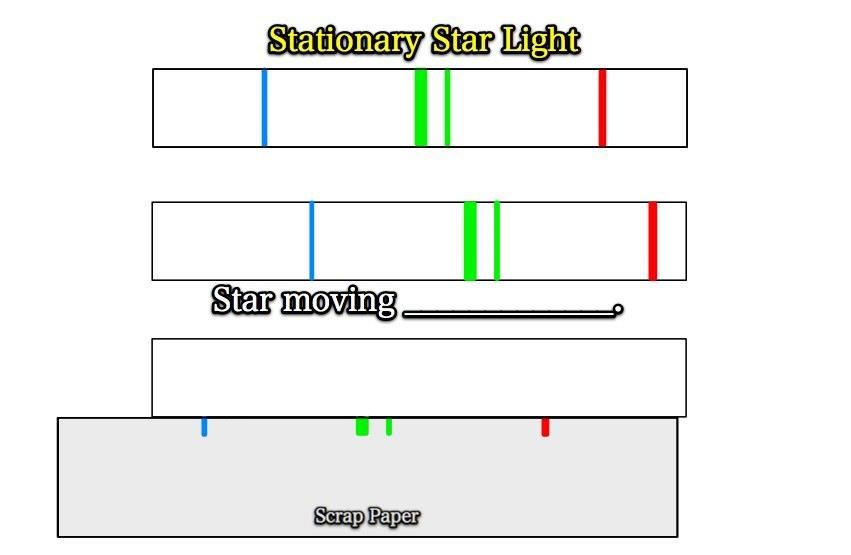
Take your scrap paper and transfer your colored lines onto the middle rectangle,
but shifted over to the left.
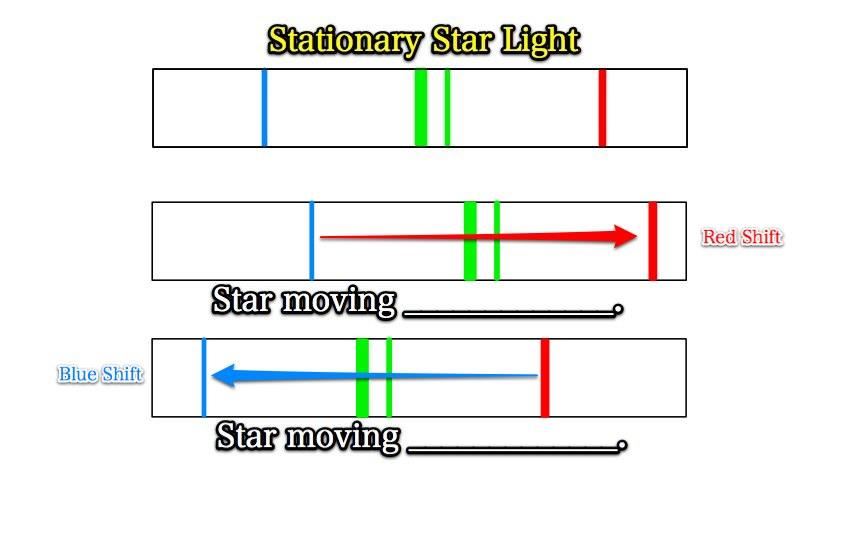
Fill in the blanks.
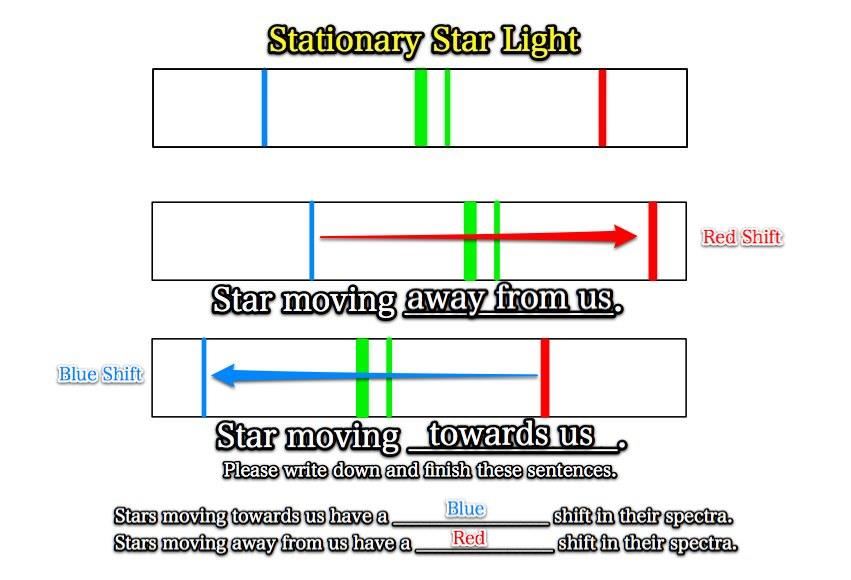
(Demonstration: Slinky and apparent light shift due to relative motion)
15. What would be an easy way to remember the difference between the Red and Blue shifts?
Blueshift = head lights = driving towards you. Redshift tail lights = driving away from you.
Redshift tail lights = driving away from you.
Important NOTE
Red and Blue spectral shifts have NOTHING to do with the temperature of a star.
The actual star's color tells us how hot it is, while the shifting of the spectra tells us how fast it is moving towards or away from us.
16. What do we know about a Red Giant star with a blue Doppler shift?
Red Giant = Big, Cool Star that is running out of fuel
Blue Shift = the star is moving towards us.
Using a star's spectral shift, we can determine the direction and speed that stars are moving, how stars revolve around galaxies, how galaxies move relative to each other, and ultimately, what is happening to the size of the Universe!
We can even tell which way our Sun rotates.
Can you?
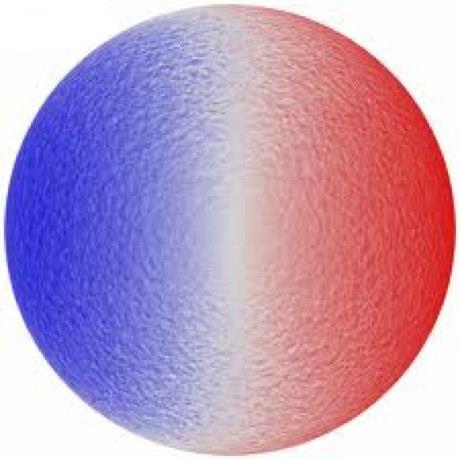
The actual Doppler effect is due to the Sun's rotation.
17. Which way does our sun rotate?
It rotates from the left to the right.
When we look out at the universe, we notice something funny about the movement of galaxies.
18. Edwin Hubble Discovered:
All distant galaxies in the visible universe are shifted RED!
19. What does this observational fact tell us about what is happening in the universe? The Universe is expanding.
20. What other things could we extrapolate from this data?
We can figure out when everything was all together.This idea became known as the Big Bang.
The Big Bang Theory
Please write this in your journal.1. Giant explosion/expansion sent everything expanding out in all directions
(still happening today)
2. Gravity clumped matter together forming galaxies, stars, planets, etc...
3. Universe is still expanding
4. Rate (speed) of expansion is increasing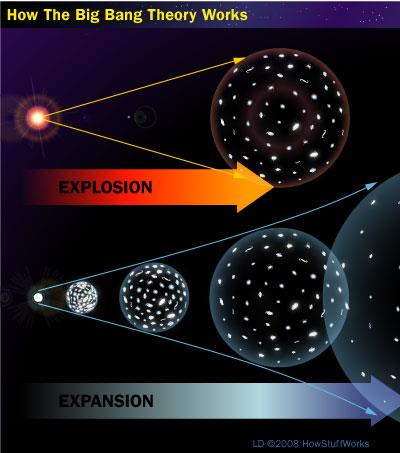
This is observationally supported by all the evidence we find in every direction that we look in outer space.
The Evidence!
21. Can we see the first light from the Big Bang?
Yes!
It is called the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation!
22. What is the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation?
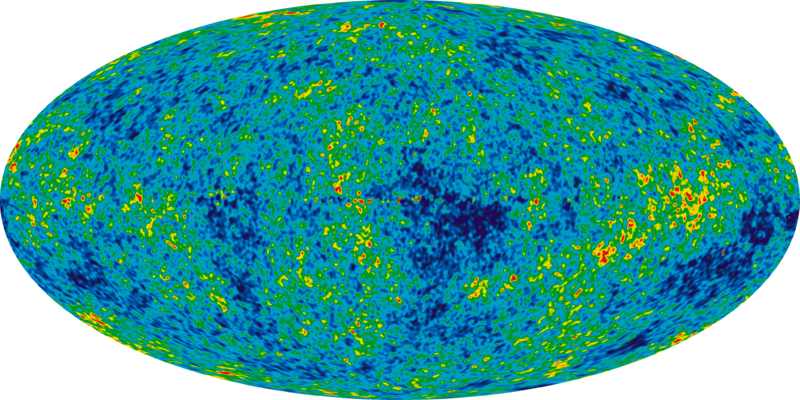
Radiation-energy left from the big bang coming from everywhere in the universe. A NASA satellite has taken a picture of the Big Bang's ancient afterglow. Scientists have analyzed the data and learned that the universe is 13.8 Billon years old and that the first stars appeared only 200 million years after the Big Bang.
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMB or CMBR) is the name given to the very dim and distant after-glow of the Big Bang coming from every point in the universe. Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson shared the 1978 Nobel Prize for Physics for their accidental discovery of the radiation made fourteen years earlier. It provides perhaps the most conclusive evidence for the Big Bang model of the universe yet.
Due to the speed of light being finite, the further out we look into space the further back we look in time. The CMB is the furthest back we will ever be able to see; it was emitted only a few hundred thousand years after the Big Bang (a blink of an eye in astronomical terms) when the universe was unimaginably hot and dense. Now it has cooled to 2.73K (-270 C).
The radiation is uniform to one part in ten-thousand in every direction. It is this uniformity that suggests so strongly that it comes from the big bang: no local source could produce it. It is only since the development of the sensitive equipment in the Cosmic Microwave Background Explorer (COBE) and it successor the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe that tiny fluctuations have been discovered and mapped.
If you could see this light every night with your eyes, the Big Bang would probably not be very controversial.23. Does the Big Bang explain the creation of the Universe?
No. The Big Bang Theory is not about the origin of the universe, it does however explain very well what happened to the universe since its beginning.
Practice Questions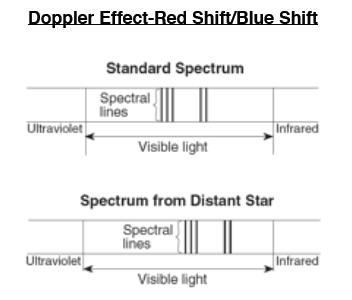
1. The doppler effect supports the idea that the universe is Expanding
2. Redshifts support the idea that objects are moving Away from one another
3. Blue shifts support the idea that objects are moving Toward one another
4. How long ago did the Big Bang occur? 13.8 Billion years ago
5. Infrared radiation is on what side of the spectrum? Longer Wavelength
6. Ultraviolet Radiation is on what side of the spectrum? Shorter Wavelength
7. The Red end of the spectrum is (long or short) wavelength? Long
8. The Blue end of the spectrum is (long or short) wavelength? Short
9. What is the name of the galaxy that we live in? Milkyway
10. What type of galaxy do we live in? Spiral
11. Galaxies that are extremely red-shifted are Extremely Far away from us.
12. Galaxies that are extremely red-shifted are moving Very Quickly away from us.
Reflection
1. Explain what the spectra of starlight tells us about the universe.2. Explain how the Doppler Effect is observed in sound and light.3. Explain what the Doppler Effect tells us about the size and age of the universe.4. Why is looking out into space like looking back in time?
BonusRecite from memory the Galaxy Song
from Monty Python's "Meaning of Life"
You can sing it in class, after school, or recite it to me from memory.
You can even do it with a partner.Galaxy Song
Just remember that you're standing on a planet that's evolving
And revolving at nine hundred miles an hour,
That's orbiting at nineteen miles a second, so it's reckoned,
A sun that is the source of all our power.
The sun and you and me and all the stars that we can see
Are moving at a million miles a day
In an outer spiral arm, at forty thousand miles an hour,
Of the galaxy we call the 'Milky Way'.Our galaxy itself contains two hundred billion stars.
It's a hundred thousand light years side to side.
It bulges in the middle, sixteen thousand light years thick,
But out by us, it's just three thousand light years wide.We're thirty thousand light years from galactic central point.
We go 'round every two hundred million years,
And our galaxy is only one of millions of billions
In this amazing and expanding universe.The universe itself keeps on expanding and expanding
In all of the directions it can whiz
As fast as it can go, at the speed of light, you know,
Twelve million miles a minute, and that's the fastest speed there is.So remember, when you're feeling very small and insecure,
How amazingly unlikely is your birth,
And pray that there's intelligent life somewhere up in space,
'Cause there's bugger all down here on Earth.
Regents Earth Science Core CurriculumPERFORMANCE INDICATOR 1.2
Describe the current theories about the origin of the universe and solar system.
Major Understandings: 1.2a The universe is vast and estimated to be over ten billion years old. The current theory is that the universe was created from an explosion called the Big Bang.
Evidence for this theory includes: • cosmic background radiation • a red-shift (the Doppler effect) in the light from very distant galaxies.
1.2b Stars form when gravity causes clouds of molecules to contract until nuclear fusion of light elements into heavier ones occurs. Fusion releases great amounts of energy over millions of years.
• The stars differ from each other in size, temperature, and age.
• Our Sun is a medium-sized star within a spiral galaxy of stars known as the Milky Way. Our galaxy contains billions of stars, and the universe contains billions of such galaxies.
1.2c Our solar system formed about five billion years ago from a giant cloud of gas and debris. Gravity causes Earth and the other planets to become layered according to density differences in their materials.
Key Idea 1: The Earth and celestial phenomena can be described by principles of relative motion and perspective.
People have observed the stars for thousands of years, using them to find direction, note the passage of time, and to express their values and traditions.
As our technology has progressed, so has understanding of celestial objects and events.
Theories of the universe have developed over many centuries. Although to a casual observer celestial bodies appeared to orbit a stationary Earth, scientific discoveries led us to the understanding that Earth is one planet that orbits the Sun, a typical star in a vast and ancient universe.
We now infer an origin and an age and evolution of the universe, as we speculate about its future. As we look at Earth, we find clues to its origin and how it has changed through nearly five billion years, as well as the evolution of life on Earth.

